Monsoon season characterized by the wet and damp climate calls for extensive care of our foot. Trudging through floods and walking through dirty water make our feet prone to accumulation of dirt, fungal infections and skin problems. Ayurveda regards foot care to be a regimen that transcends cosmetic purposes and benefits the nervous system in a great extent.
Here are effective tips foot care in the monsoon season.
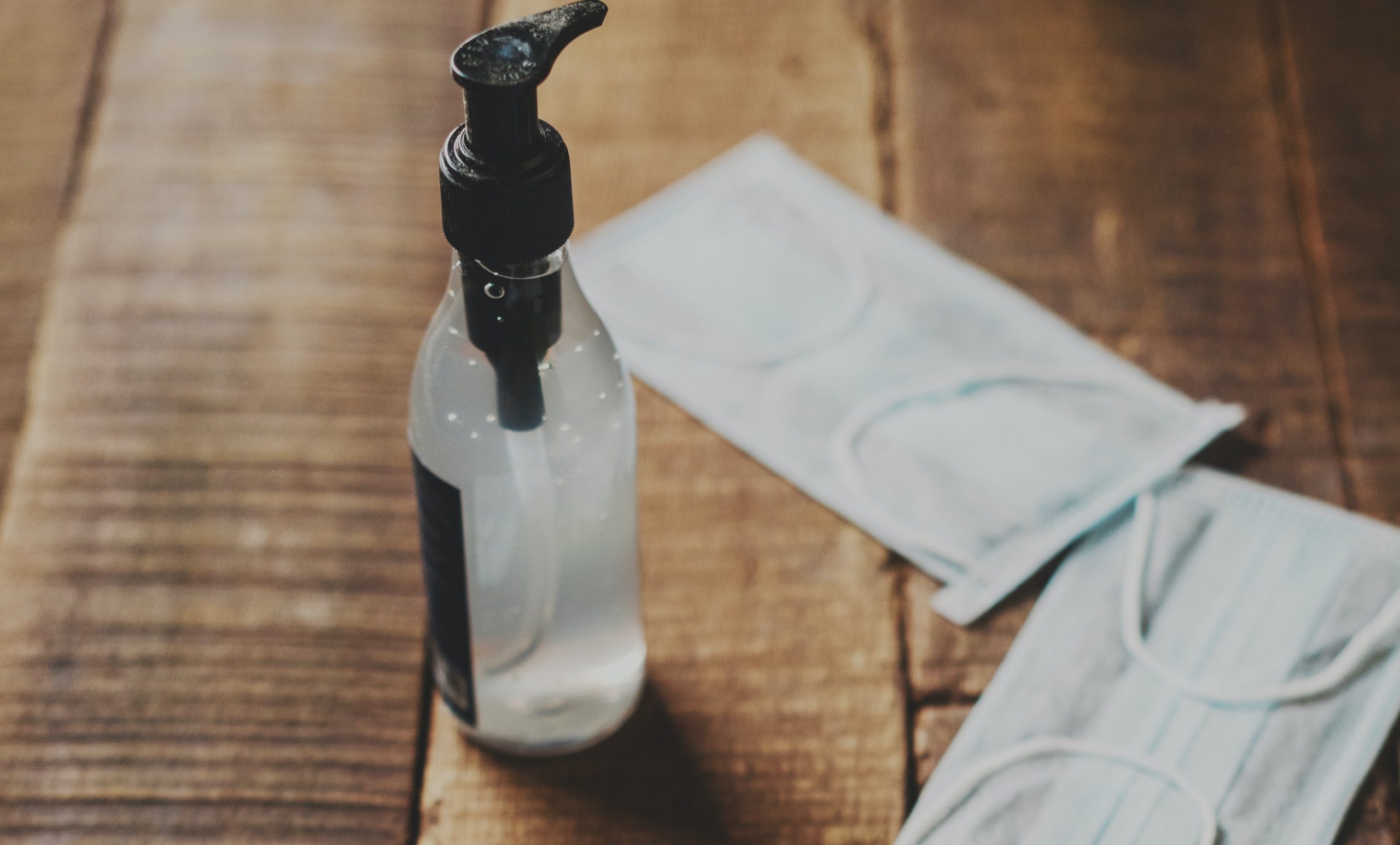
• Keep your feet clean and dry – Ensure that your feet is kept dry at all times as wetness especially between the toes can result in fungal infections. Also, the continuous exposure to water can make the feet soggy and prone to cracks. Trimming toenails is also vital to prevent the accumulation of dirt and germs.
• Comfortable footwear – Prefer open footwear like flip flops or sandals which let the feet breathe. Tight and closed shoes when wet can be the breeding ground of bacteria and fungus.
• Exfoliate – Removing dead skin from the feet is important to prevent them from hardening up and causing cracks. Use a foot scrubber or a pumice stone to exfoliate your feet daily.
• Moisturize – The damp atmosphere is no reason for the skin to be left dehydrated. Moisturise your feet after bath in the morning and before bed at night. Olive oil and almond oil are effective natural moisturisers.
• Dry the footwear – Wet footwear should be kept in the sun and allowed to dry properly before using again. They should not be stored under the bed or in the shoe cupboard as the damp environment and the dark canattract fungus and bacteria.
• Foot bath – Ensure proper foot care with an herbal foot bath once in a week. Mix in sea salt to a bucket of warm water and soak your feet in it.Then scrub the feet using a pumice stone to exfoliate. Adding rose water or aromatic oils to the water is also beneficial.
• Foot massage – Ayurveda highly recommends foot massages for overall health as it helps improve blood and lymph circulation, detoxifies the body, balances the doshas and promotes a healthy nervous system.
Latest posts by Dr.Sandeep Krishna (see all)
- Covid 19 Measures - August 21, 2020
- How to Boost your Immune System with Ayurveda? - April 1, 2020
- 10 Superfoods to keep you cool during the Summer Season - March 25, 2020